PCB Headers & Interconnects
Overview
Headers and mating sockets form the mechanical and electrical bridge between the device under
test and the system hosting it. Properly selected interconnect hardware improves contact
reliability, protects the PCB, and enables modular adapter and fixture designs.
Repeatable Engagement
Consistent mating improves signal integrity and reduces wear on the target PCB.
Serviceable Interfaces
Interconnects can be replaced or reconfigured without redesigning the adapter.
Modular Stack Height
Clearance can be built in for dense layouts, tall components, or retention hardware.
Interconnect types
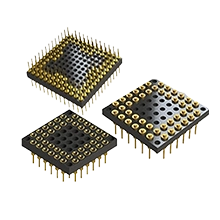
BGA / LGA Headers & Mating Female Receptacle Sockets
stacks, clearance management, and fixture-friendly interfaces.
DIP Headers & Mating Sockets
and production replacement applications.
PGA Headers & Mating Sockets
Pin-grid interconnects for high pin-count devices where engagement consistency
and mechanical stability are critical.
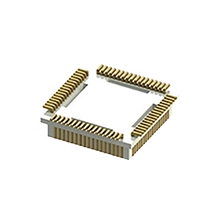
PLCC Emulator Plugs
emulation and programming applications.
Specifying the Correct Interconnect
Selecting the appropriate header and mating socket starts with understanding the device
interface, PCB constraints, and intended use. In many cases, existing footprints can be reused,
or a new footprint can be defined to match specific mechanical or electrical requirements.
Device Interface
- Package type and pin or ball count
- Pitch and orientation
- Keying or alignment features
PCB Constraints
- Existing footprint or land pattern
- Component keep-out zones
- Required stack height
Use Case
- Prototyping, production test, or burn-in
- Insertion cycle expectations
- Handling or environmental constraints
Custom & Technical Guidance
When standard configurations are not a perfect fit, our engineering team designs and builds
custom interconnect solutions to match your footprint, stack height, and mechanical
requirements. Built-to-order solutions typically ship in 2–4 weeks, depending on complexity.